Eligibility Process Guide: Benefits Coverage Workflow
Eligibility Process Guide: Benefits Coverage Workflow
1. Overview: Understanding Patient Entitlements
This guide outlines the Benefits Coverage workflow, an essential part of the Eligibility Process. Once a patient has been accurately identified through the Patient Search workflow, this stage determines the specific healthcare services and interventions they are entitled to receive. This determination is based on the patient's biodata, their contributions to the Social Health Authority (SHA), whether they are a civil servant, and the facility they visited. All of this information is cross-checked against the rules established by SHA.
1.1. What This Workflow Does
The Benefits Coverage workflow dynamically cross-checks information on the patient and facility versus the eligibility rules and then retrieves the specific sub-benefits a patient is eligible for. It does this by taking several key pieces of information:
- Patient Details: Crucial information like their age, gender, and especially their contribution status with SHA.
- Facility Details: Information about the healthcare facility where the service is to be provided, such as its ownership (e.g., public, private), its KEPH level, licensure, and SHA contract status.
The system applies a set of rules from the SHA benefit matrix—essentially a rulebook that dictates which services are covered under various patient and facility conditions.
1.2. Why This Workflow Is Critical
- Risk of Uncovered Services: Prevents patients from incurring unexpected costs.
- Financial Loss for Providers: Avoids services for which facilities won't be reimbursed.
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Ensures adherence to SHA policies.
- Improved Patient Experience: Patients know what they are entitled to upfront.
2. Benefit Matrix Overview
2.1. Overall Benefit Structure
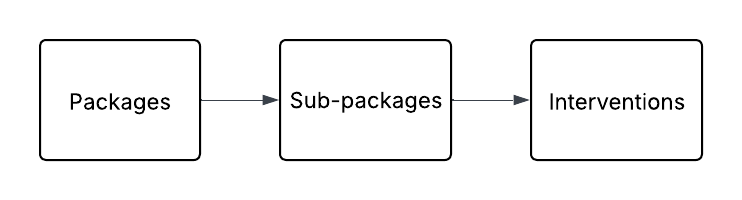
- Packages: Highest level, e.g., inpatient/outpatient.
- Sub-packages: Breakdown by common characteristics, e.g., emergency services.
- Interventions: Specific healthcare services, each with limits and tariffs.
2.2. Funds
- Primary Healthcare Fund (PHC): Covers outpatient services at lower-level facilities, funded by government and grants.
- Social Health Insurance Fund (SHIF): For contributing members, available at hospital level 3 and above.
- Emergency Chronic Critical Illness Fund (ECCIF): For emergency, critical, chronic, and palliative care.
2.3. Schemes
- UHC (Universal Healthcare Coverage): For all citizens using PHC and SHIF.
- PMF (Public Medical Officer Fund): For civil servants, extended coverage.
2.4. Payment Mechanisms
- Capitation: For PHC, based on patient numbers at facilities.
- Per Diem: Daily payments, e.g., ICU care.
- Fee for Service: SHA pays full fee if tariff is met.
- Fixed Fee for Service: SHA pays fixed fee; patient covers the rest.
- Case-Based: Depends on treatment scenario; e.g., cesarean after failed normal delivery.
ECCIF and SHIF use all payment mechanisms except capitation.
3. Workflow Details: Benefits Coverage
3.1. Workflow Description
- Input Reception: Takes Client Registry ID (CR ID), facility ID and optionally service type.
- Internal Data Retrieval: Fetches full patient profile and facility details.
- Rule Application: Applies SHA benefit matrix:
- Patient vs benefit categories.
- Facility vs licensed services.
- Sub-Benefit Determination: System compiles eligible sub-benefits.
- Outcome Delivery: Returns the list.
3.2. Key Validations
- Valid Facility ID & Type: Must be known and accurate.
- CR ID is Mandatory: Identifies the patient and their eligibility.
- Facility ID Type Must Be Recognised: e.g.,
fr-code,registration-number. - Valid Age and Gender: Needed for SHA age- and gender-based rules.
- CR Only Source for Patient Data: Ensures single source of truth.
- Facility Must Meet SHA Criteria: Includes KEPH level, ownership, contract status.
3.3. Workflow Data Dictionary
| Field Name | Description | Data Type | Required | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beneficiary Client Registry ID | Unique patient identifier from Patient Search | String | Yes | Used to retrieve profile and apply rules |
| Facility Identifier | Unique ID for health facility | String | Yes | Required to determine eligible services |
| Facility Identifier Type | e.g., fr-code, registration-number | String | Yes | Helps system interpret facility ID |
| Service Type | e.g., INPATIENT, OUTPATIENT | String | Yes | Context for the check |
| Sub-Benefit Code | Optional code for a specific benefit | String | No | If specified, limits search to one item |
3.4. Expected Outcomes
- Successful Retrieval of Benefits: Patient is eligible, list of sub-benefits returned.
- No Benefits Found: Valid patient/facility but no matched sub-benefits.
- Input Error: Invalid or missing data prevented execution.
4. Critical Success Factors for Benefits Coverage Integration
- Keep IDs Updated: Use the latest
beneficiary_cr_id,facility_id, andfacility_id_type. - Understand SHA Rules: Know how demographics and facility affect results.
- Handle “No Benefits Found” Gracefully: Design for fallback messaging or user alerts.

